9 Performance Aspects
Abschlussbedingungen
Gesamtpunktzahl: 0 / 0
9 Performance Aspects
The main
features of mobile communication are the radio transmission between the MS and
the BS and the use of the analog radio channel for digital data transmission.
The analog channel „air“ leads to fading field strength, shadowing, attenuation,
and interferences from co- and adjacent channels. In digital transmission this
means high bit error rate, burst errors and time and location dependent
fluctuation.
Because of the limited bandwidth only a small transmission rate can be achieved. The frequencies of GSM need to be reused making frequency planning an important task. The small number of channels per base station results from the small total number of channels and results in higher blocking probability. Together with the movement patterns this has to be taken into consideration for transmission power and power control, interference minimization, battery power control and EMC (ElectroMagnetic Compatibility) constraints.
Service access performance denotes the ability of a service to stay between tolerable values while reaching the service.
Performance of service maintenance means the ability of a service to stay reachable for the wanted duration at an acceptable service level.
Users have
the following performance criteria:
Because of the limited bandwidth only a small transmission rate can be achieved. The frequencies of GSM need to be reused making frequency planning an important task. The small number of channels per base station results from the small total number of channels and results in higher blocking probability. Together with the movement patterns this has to be taken into consideration for transmission power and power control, interference minimization, battery power control and EMC (ElectroMagnetic Compatibility) constraints.
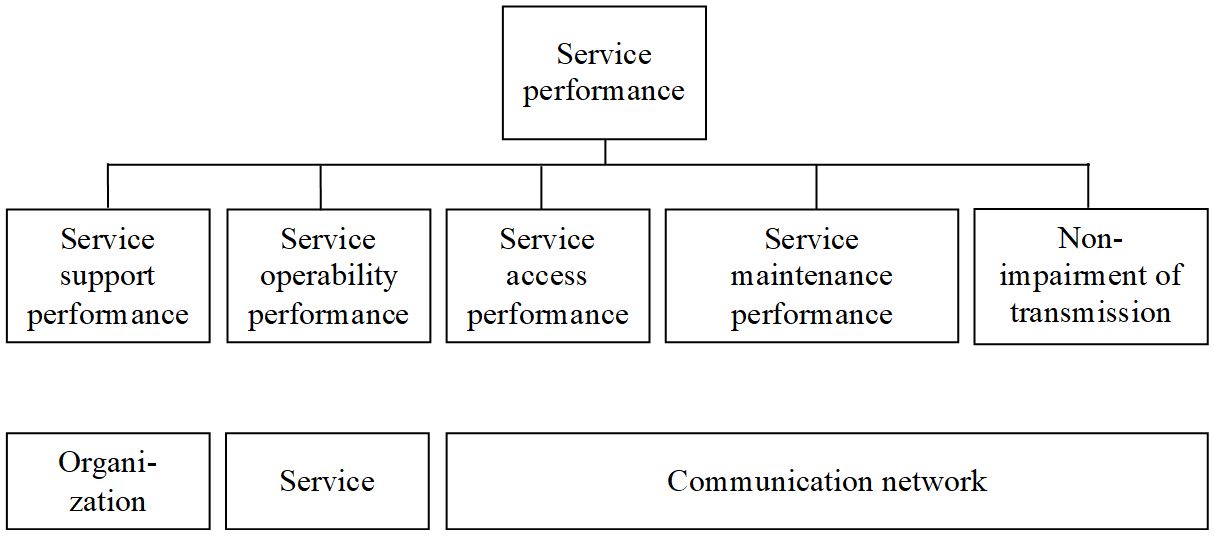
Figure 9-1: Quality of telecommunication services from
CCITT E.800.
Service
support performance means the ability of one or more organizations to provide
services tailored to the users and to support their use. The service support
performance is judged by customer satisfaction, e.g. by customer interviews,
complaints received by organizations or test from test-users. One can judge
available tele, supplementary and value added services, available user
equipment, installation, maintenance, helpdesk and planning of service subscription,
prices for service subscription and usage, billing.
Service
operability performance denotes the
simplicity to use a service, including features of the user equipment, the
comprehensibility of tones and messages. The operation is judged by frequency
of wrong user reaction during a service by probability of errors setting up a
service, calling the wrong number, stopping the attempt and stopping of
dialing.Service access performance denotes the ability of a service to stay between tolerable values while reaching the service.
Performance of service maintenance means the ability of a service to stay reachable for the wanted duration at an acceptable service level.
Non-impairment of a service gives the grade up to which a
service (once reached) can be offered with accordable effort.
- Speed – How long do they have to wait?
- Accuracy – Is the execution correct?
- Reliability – Can one rely on correct execution?
- Mobility and movement – Where can the user access the communication? How mobile can the user be during the communication?
- Security – Is the communication
private and confident?
Tab. 9-1: Performance.
|
User oriented performance of |
||
|
Access phase |
Information transfer phase |
Termination phase |
|
Speed |
||
Duration until
| Delay Transmission rate Throughput | Duration until next use of the service is possible |
|
Accuracy |
||
|
Rate of wrong connections |
Transmission quality |
Probability of incorrect termination Difference to exact duration of
use of service |
|
Reliability
|
||
|
Probability for missing network answer Blocking rate Standby time for user equipment |
Rate for early service termination Percentage of long disruption Probability for information loss Duration of terminal use |
Denial of termination |
|
Mobility and movement
|
||
|
Locations where the service can be used |
Coverage degree and performance Max. speed of movement Agility while service |
|
|
Security
|
||
|
Measurement for protection of transmitted signaling information |
Measurement for protection of transmitted signaling information
Measurement for confidentiality of transmitted user information |
Measurement for protection of transmitted signaling information |
Examples
for performance criteria and target values for network oriented performance
from GSM 02.08:
- Time between service request and use (MS calling)
- BCCH known 4 s
- BCCH unknown 10 s
- Rate of successful called services (MS calling) > 99%
- Connection setup time between MS and PLMN border 4 s
- Time until confirmation of connection request 1 s
- Time until connection termination between MS and PLMN border 2 s
- Rate of successful called MS > 99%
- Time until MS is activated (MS called)
- First attempt 4 s
- Last attempt 15 s
- Time until first use or change of a supplementary service 10 s
- Interruption because of handover
- MSC-MSC handover 150 ms
- BS-BS handover inside one MSC area 150 ms
- Change of channel inside one BS 100 ms
- Change of time slot inside one channel of one BS 100 ms
- Interruption of user data (if not caused by handover) 40 ms
- Rate of successful handovers > 99%